Context
Antibiotic resistance is a major public health problem impacting human health, animal health and environmental ecosystems. Effectively combating antibiotic resistance requires a One Health approach that takes into account the dependence between these three health conditions. However, putting this approach into practice remains difficult as the three sectors concerned are so different.
This is why, as part of its missions, PROMISE wanted to set up a cross-sectional and cross-sectoral analysis of resistance and uses (consumption data) relating to antibiotics in France.
Objectives and key figures
This analysis made it possible to cross-reference aggregated data from 12 human and animal health surveillance systems. The objective is to evaluate possible correlations between consumption and resistance for different bacteria – antibiotic pairs.
This analysis represents a real national collaboration between several surveillance systems, with a pooling of data. In a few figures, this gives:
- 12 aggregated monitoring devices;
- 6 bacterial species monitored;
- 5 established resistance families;
- 1 new indicator highlighted;
- 10 years of data collected;
- …and very encouraging preliminary results.
Related media [FR]
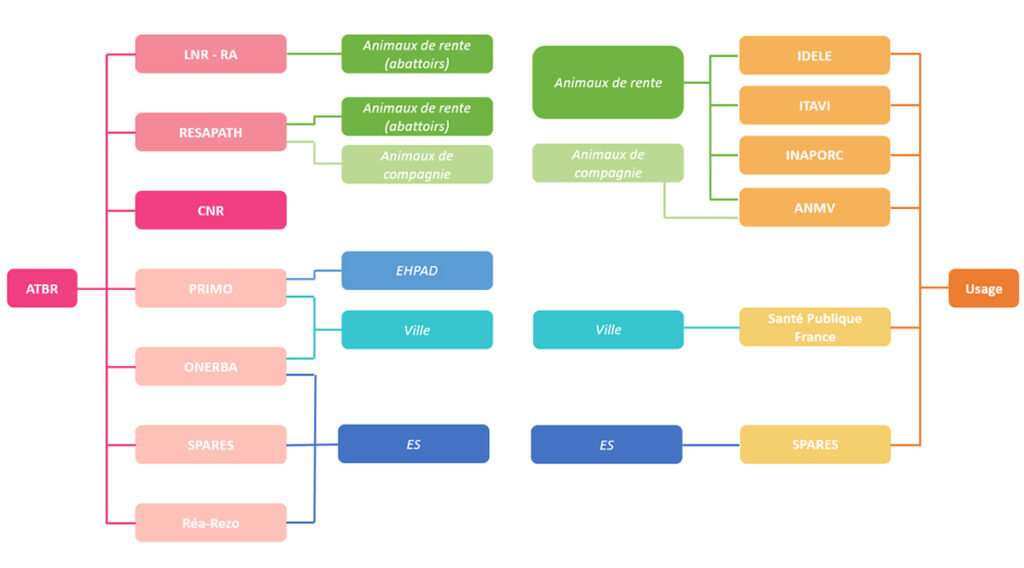
Surveillance systems contributing to PROMISE’s cross-sectoral analysis
In pink are the devices collecting resistance data. In orange, the devices collecting consumption data are represented. In the center are indicated the sectors for which each device collects data. Animal health is shown in green and human health in blue.
Abbreviations used: EHPAD = Accommodation establishment for dependent elderly people ; ES = Health establishment.