Context
Antibiotic resistance concerns people, animals… but also the environment. It is a phenomenon that knows no borders and also affects ecosystems. This is the case, for example, of water, largely contaminated by antibiotics, their residues, bacteria and resistance genes coming from a main source, urban wastewater treatment plants. If antibiotic resistance is the subject of more and more studies within the human or animal sphere, this is less the case in the environmental world: but we must not forget that it is a threat to all of life.
This is why, as part of its missions, PROMISE wishes to demonstrate the feasibility of a monitoring system for antibiotic resistance in the environment in France.
Objectives and key figures
PROMISE is carrying out a feasibility study whose objective is to establish common indicators and protocols to quantify antibiotic resistance in the environment. It is therefore based on the selection of relevant monitoring indicators as well as the definition of standardized measurement protocols for its indicators, i.e. a standardization of sampling and analysis procedures to make the data produced interoperable.
AMR-Env, one of the PROMISE working groups, is responsible for this study. It is made up of 22 research units spread across France and 4 networks:
- OZCAR : Critical Zone Observatories – Applications and Research;
- GRAIE : Research group, technical animation and information on water;
- PNDB : National biodiversity data center;
- Water Agencies.
Today, the feasibility study highlights an inter-laboratory validation protocol between 5 research units. At the same time, encouraging results are underway: on the one hand, the definition of a reproducible method (little deviation from one laboratory to another) and on the other hand, validation of several common indicators is well underway.
Related media [FR]
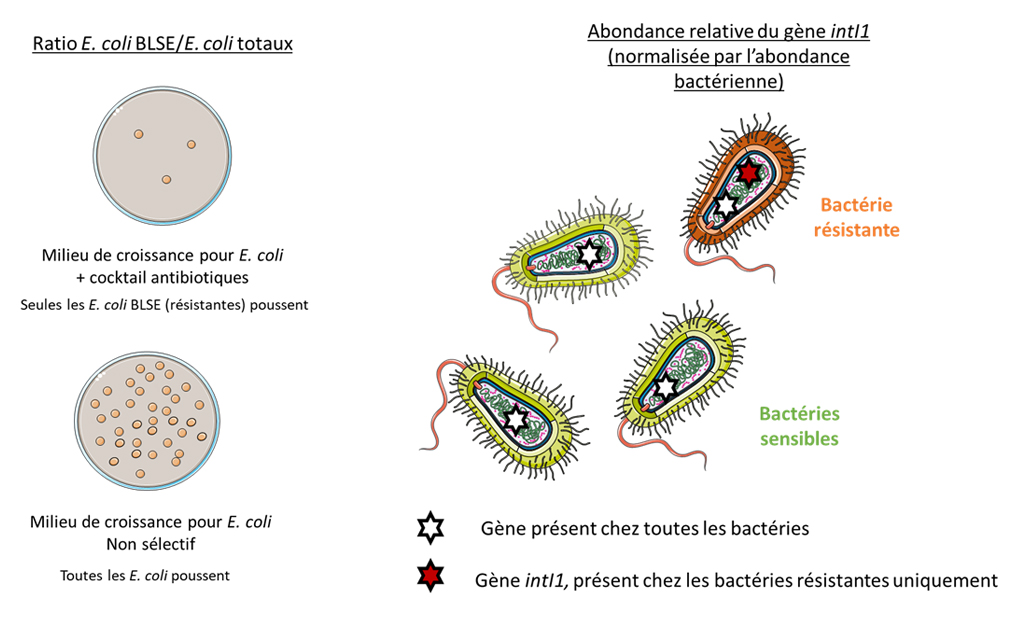
Initial illustration of the preliminary indicators for monitoring antibiotic resistance in the environment selected
The feasibility study focuses on six common indicators selected: E. coli ESBL (culture method); E. coli 16S RNA (qPCR, fecal contamination); intI (qPCR, global resistance indicator); aacA4 (qPCR, human contamination marker) and aadA/aadB (qPCR, animal contamination marker).